

As global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) continue to evolve, antenna selection has become a critical design decision for engineers and system integrators. Whether you are developing a vehicle positioning system, a precision agriculture solution, a UAV platform, or an IoT tracking device, the choice between dual-band GNSS antennas and multi-band GNSS antennas can significantly impact positioning accuracy, reliability, and overall system performance.
This article explores the differences between dual-band and multi-band GNSS antennas, explains how each performs in real-world applications, and provides practical guidance to help you choose the right solution based on your technical and commercial requirements.
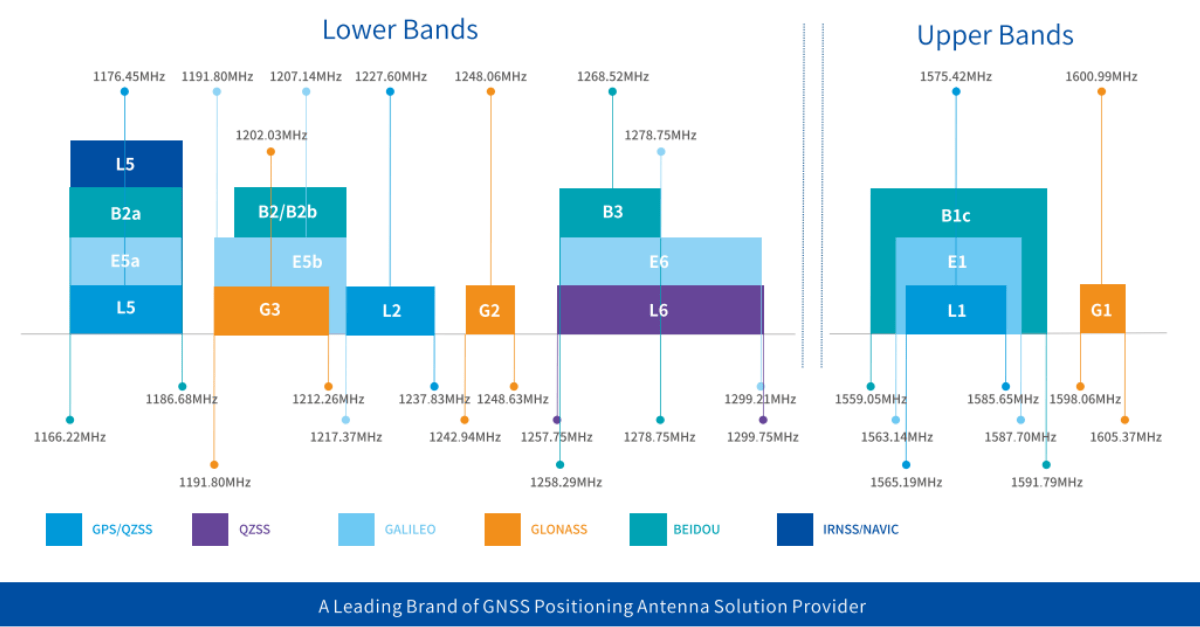
GNSS positioning relies on signals transmitted by multiple satellite constellations, including GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, BeiDou, and QZSS. These signals are broadcast across different frequency bands, with the most commonly used being:
L1 / E1 / B1 – widely used, good global availability
L2 / E5b / B2 – improves accuracy and ionospheric error correction
L5 / E5a – higher signal power, better resistance to interference
Modern GNSS antenna selection increasingly focuses on how many of these bands an antenna can receive simultaneously.
A dual-band GNSS antenna is designed to receive signals on two frequency bands, most commonly L1 + L2 or L1 + L5. By tracking two frequencies at the same time, the receiver can significantly reduce ionospheric delay errors, which are one of the largest contributors to positioning inaccuracy.
Supports two GNSS frequency bands
Better accuracy than single-band antennas
Lower cost and simpler design than multi-band antennas
Lower power consumption
Widely used in mass-market and professional applications
Dual-band GNSS antennas are often considered the entry point for high-precision positioning, especially in systems where size, cost, and power efficiency matter.
A multi-band GNSS antenna supports three or more frequency bands across multiple satellite constellations. These antennas can receive signals such as L1, L2, L5, E5a, E5b, and B2, enabling advanced positioning techniques and higher robustness in challenging environments.
Tracks multiple frequency bands simultaneously
Supports more satellite signals at any given time
Superior multipath mitigation
Improved availability in urban or obstructed environments
Ideal for RTK, PPP, and high-precision surveying
Multi-band antennas are increasingly used in centimeter-level positioning systems, where reliability and accuracy are non-negotiable.
Dual-band GNSS antennas already offer a significant leap over single-band solutions by compensating for ionospheric delays. For many applications, this level of accuracy—often sub-meter to decimeter—is sufficient.
Multi-band GNSS antennas go a step further. By receiving more frequencies from multiple constellations, they enable faster ambiguity resolution and higher positioning stability, especially when used with RTK (Real-Time Kinematic) or PPP (Precise Point Positioning) techniques.
Summary:
Dual-band: good accuracy for most professional applications
Multi-band: best choice for high-precision and mission-critical systems
In open-sky environments, both antenna types perform well. However, in urban canyons, forested areas, or industrial sites, signal blockage and multipath interference become serious challenges.
Multi-band GNSS antennas can track a larger number of satellites across different frequencies, increasing the chance of maintaining a reliable position fix even when some signals are degraded.
Summary:
Dual-band: reliable in moderately challenging environments
Multi-band: superior performance in harsh or obstructed conditions
Dual-band antennas usually support major constellations such as GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and BeiDou on two main frequencies.
Multi-band antennas are designed for full-constellation, full-frequency compatibility, making them more future-proof as new GNSS signals are deployed.
This is especially important for long-life products such as surveying equipment, base stations, and autonomous systems.
From a hardware perspective, dual-band GNSS antennas are generally:
Smaller in size
Easier to integrate into compact devices
Less demanding in terms of RF layout
Multi-band antennas require more complex RF design, precise phase center control, and careful ground plane optimization. While this increases design complexity, it also enables much higher performance.
Manufacturers with deep GNSS expertise—such as Harxon, known for its professional GNSS antenna portfolio—invest heavily in antenna simulation, testing, and phase center optimization to ensure consistent performance across all supported bands.
Cost is often a decisive factor.
Dual-band GNSS antennas are more affordable and suitable for volume production.
Multi-band GNSS antennas typically come at a higher price due to more complex design, tighter tolerances, and advanced performance requirements.
However, in high-precision applications, the added cost of a multi-band antenna is often justified by reduced downtime, faster convergence, and improved data quality.
Dual-band GNSS antennas are ideal for:
Fleet management and vehicle tracking
UAV navigation and control
Smart agriculture machinery
GIS data collection
IoT positioning devices
In these scenarios, dual-band antennas provide an excellent balance between performance, cost, and power efficiency.
Multi-band GNSS antennas are recommended for:
RTK base stations and rovers
Precision agriculture (centimeter-level accuracy)
Deformation monitoring and reference networks
For these use cases, the performance advantages of multi-band reception directly translate into higher productivity and reliability.
Both dual-band and multi-band GNSS antennas can be active or passive.
Active GNSS antennas include a built-in low-noise amplifier (LNA), making them suitable for long cable runs and low-signal environments.
Passive GNSS antennas rely on external amplification and are often used in compact embedded systems.
High-quality active GNSS antennas—such as those offered by Harxon—are designed with optimized noise figure and out-of-band rejection, ensuring clean signal reception even in RF-noisy environments.
The GNSS industry is clearly moving toward multi-band, multi-constellation solutions. As correction services become more accessible and demand for high-precision positioning grows, multi-band antennas are becoming the standard in professional and industrial markets.
That said, dual-band GNSS antennas will continue to dominate cost-sensitive and space-constrained applications for years to come.
Choosing between a dual-band and a multi-band GNSS antenna is not about selecting the ''better'' technology—it's about selecting the right tool for your application.
If your project prioritizes cost efficiency, compact design, and solid performance, a dual-band GNSS antenna is often the best choice.
If your system demands maximum accuracy, reliability, and long-term scalability, investing in a multi-band GNSS antenna is the smarter decision.
Working with experienced GNSS antenna manufacturers such as Harxon can help ensure that your antenna choice aligns with both current requirements and future system upgrades.